Form layout components in Ember and the related Form “Template” component in Figma are structural components that provide the scaffolding for building standardized forms across products. These components establish spacing and layout standards to give users a consistent experience.
Usage
When to use
- To structure and organize form elements and inputs into a consistent layout
- When creating a form of any size in our products, including forms nested within Flyout or Modal components
When not to use
- To organize non-form content
- To create a form for key-value pairs, use the Key Value Inputs component
Form
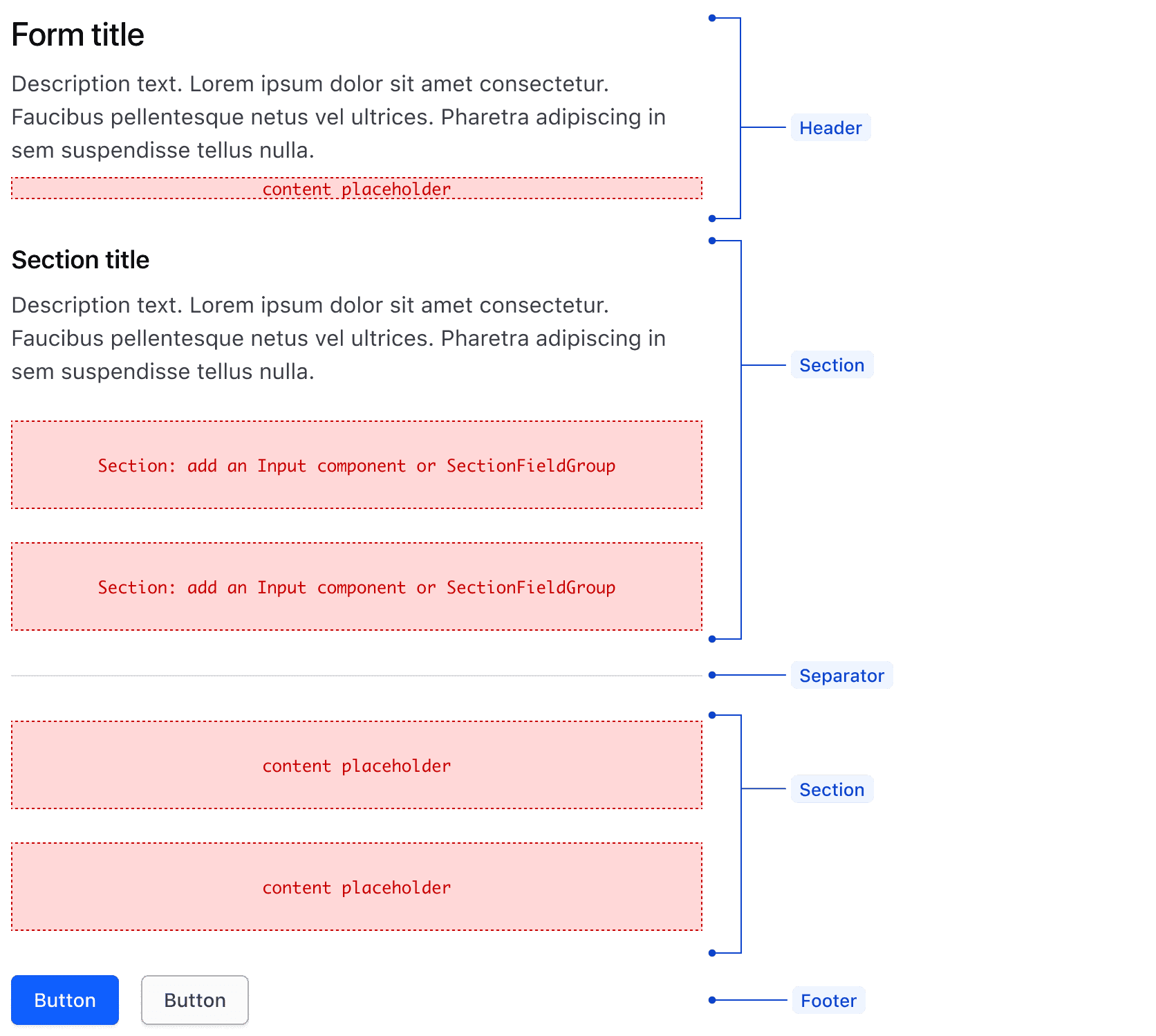
The Form component serves as the container for all Form layout components and form content. It establishes the spacing between the Form Header, Sections, Separators, and Form Footer.
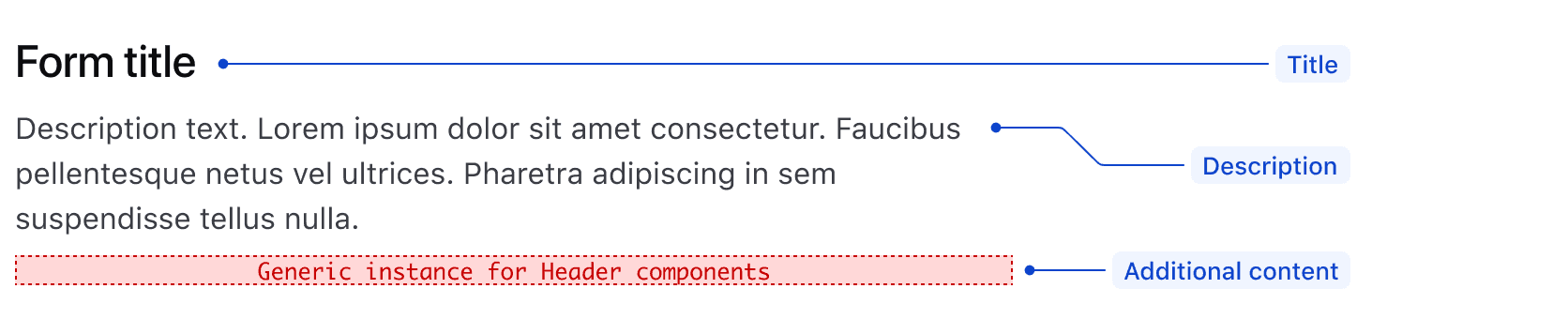
Form Header
The Form component has an optional header with styled text for a Title and Description. It also includes a space for custom content to use as needed.
Form-level error alert
Conventionally, input level validation is sufficient for error messaging within a form but overarching form-level messaging may be needed if validations happen on submission. Form-level error alerts should be applied in the case of form-level submission failures, timeouts during data submission, or when errors apply to multiple sections within the larger form.
The form-level error message will appear below the Header as its own Section and uses the Alert component.
Form Section
Inputs within a form are organized in Sections. Multiple Sections may be used to group content for a more scannable and organized experience. Inputs that belong under the same heading or are related to the same topic should be within a Section.
Section Header
Similar to the Form Header, the Section Header contains styled and spaced text elements, and a space for custom content to be used as needed.

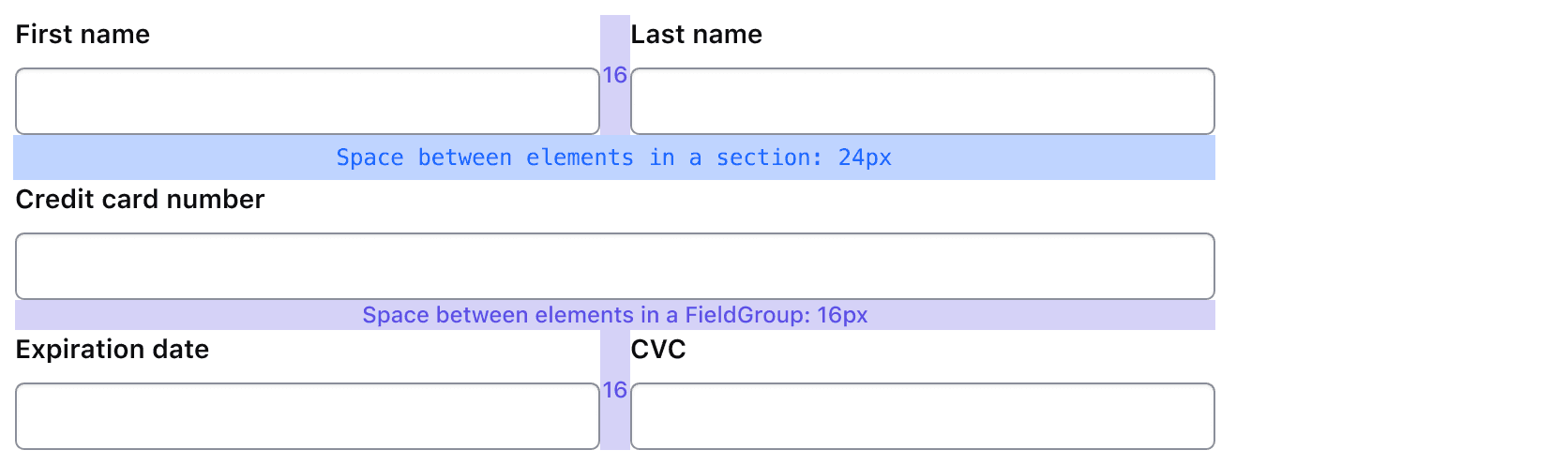
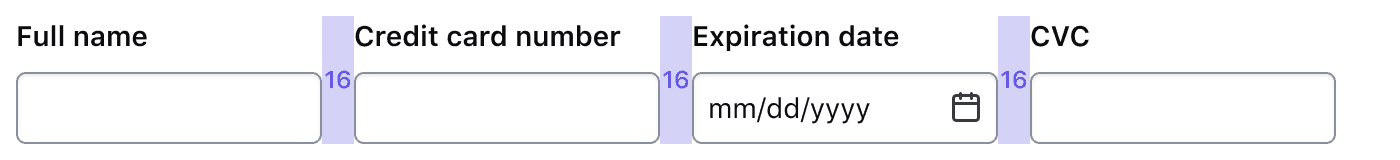
Section Multi Field Group
The Section Multi Field Group organizes closely related form inputs in a single row, setting 16px between them, as opposed to 24px when stacked. This reinforces their relationship.
When the viewport width falls below the “md” breakpoint, inputs contained in a Section Multi Field Group automatically stack.
Organize inputs together when they are closely related and beneficial to read together. No more than three inputs should be put within a single row.
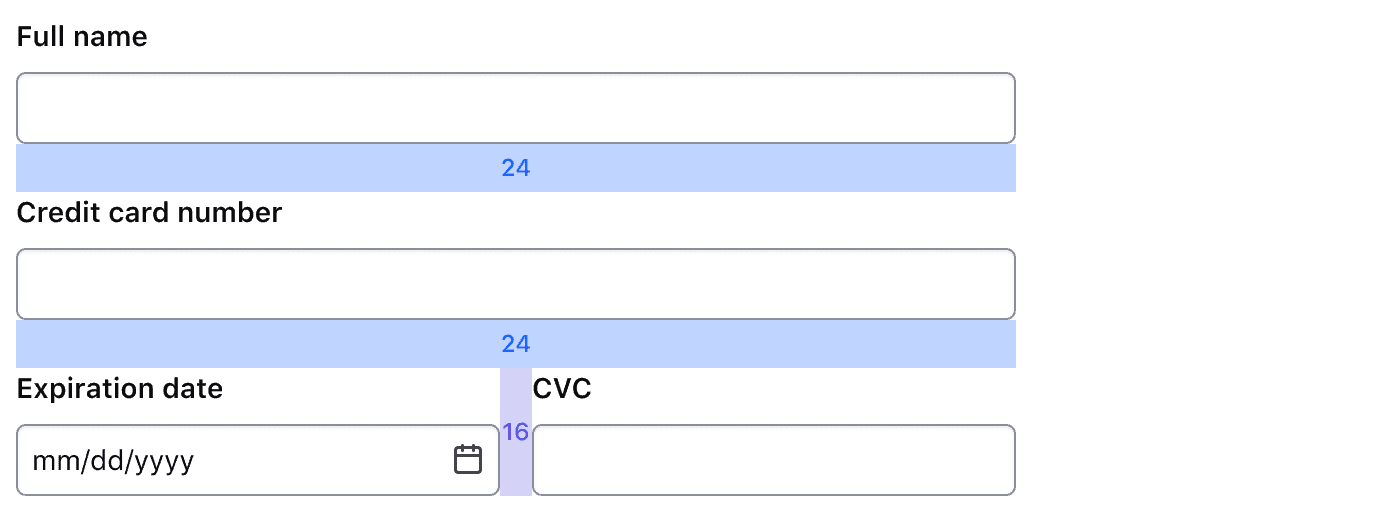
Place inputs in rows to save space or create columns within the form.
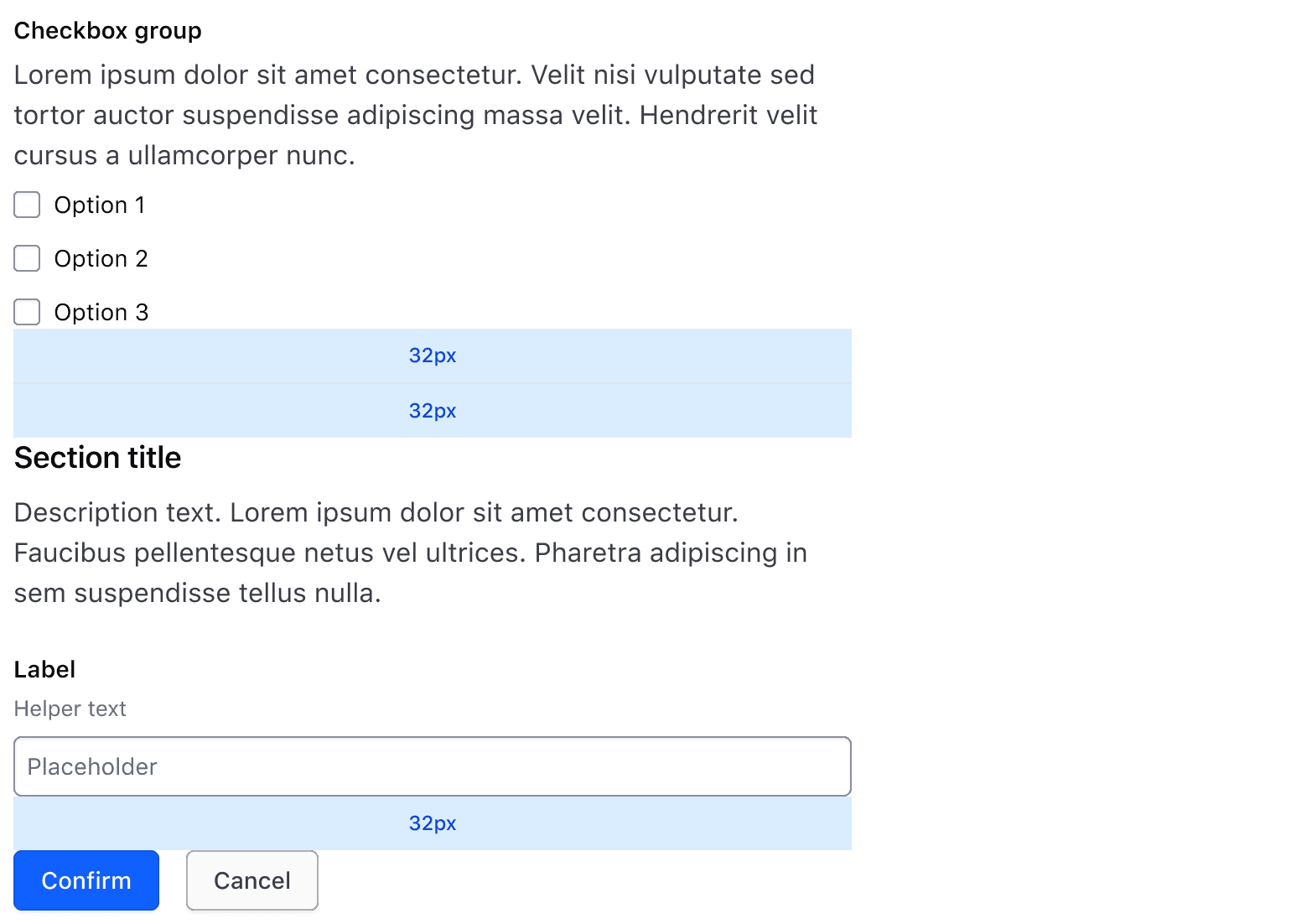
Form Separator
A Separator can be placed between Sections when a clearer visual distinction between Sections is needed.
Use a Separator to add space between Sections or before a new Section Header.
Don’t use a Separator between the last Section and Form Footer / Button Set.
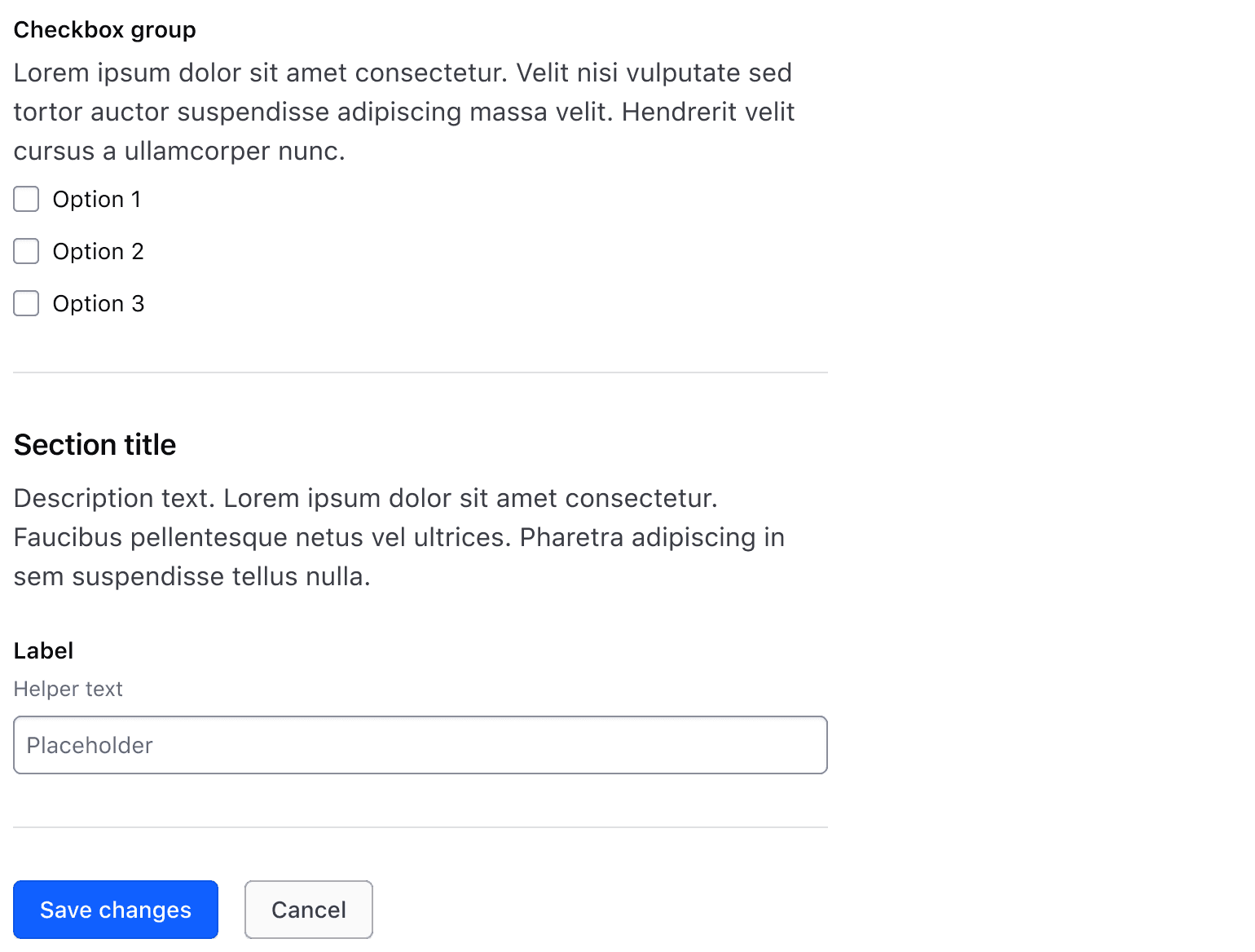
Form Footer
The Form Footer typically houses Buttons to allow users to submit form information. When there's more than one Button or action, we recommend using the Button Set component for consistent spacing and layout.
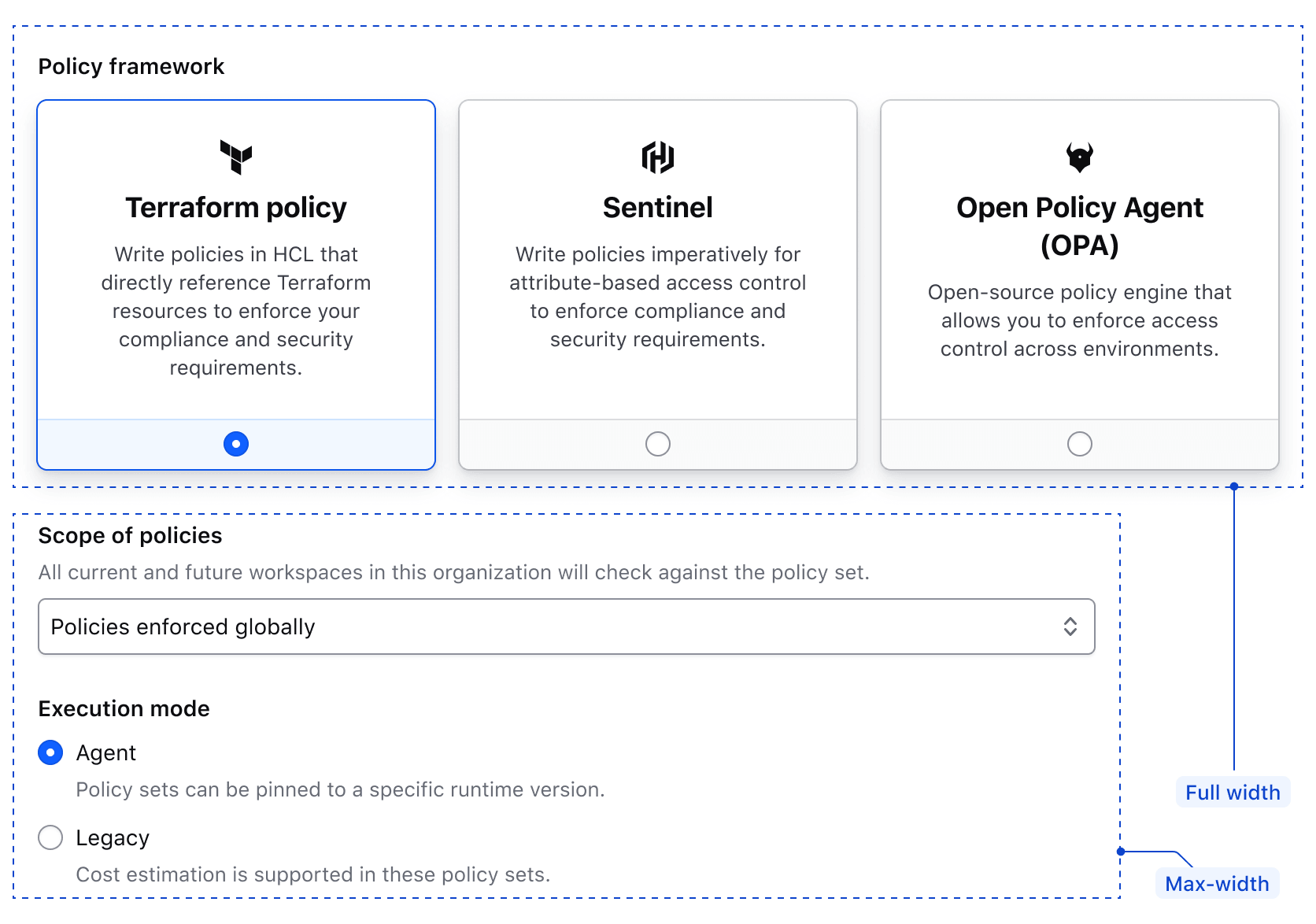
Width and resizing behavior
Max-width
Sections have a default max-width of 672px, establishing a consistent line length throughout applications. It's possible to customize this max-width value if needed.
Full-width
Individual Sections can be set to full-width, if needed. Any component requiring increased width for usability, e.g., a Radio Card Group, should be moved into a separate Section to allow for full width layout, even if they would otherwise be grouped with other associated fields.
How to use this component
Use the Form to contain other Form layout components and form content. This establishes consistent spacing for each FormSection and the other content.
Form
<Hds::Form>
Add form content here.
</Hds::Form>
The Form renders as an HTML form element by default. Use the tag argument to optionally use an HTML div instead.
<Hds::Form @tag="div">
This “form” is actually just a div.
</Hds::Form>
Form Header, Title, & Description
Use the optional FormHeader to include a Title and Description for your Form.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Header>
<FORM.HeaderTitle @tag="h2">My form title</FORM.HeaderTitle>
<FORM.HeaderDescription>A brief description of my form content.</FORM.HeaderDescription>
</FORM.Header>
</Hds::Form>
Form Header Title tag & size
The @tag argument changes the HTML element that wraps the FormHeaderTitle content. When organizing the content on a webpage, the heading levels should reflect the structure of the page. For example, if a FormHeaderTitle appears directly below the main heading of the page, it should be "h2".
To specify which size the FormHeaderTitle displays at, use the @size argument.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Header>
<FORM.HeaderTitle @tag="h3" @size="300">My form title</FORM.HeaderTitle>
<FORM.HeaderDescription>A brief description of my form content.</FORM.HeaderDescription>
</FORM.Header>
</Hds::Form>
Form Section
Use FormSection components to wrap and group together related Form Fields and other form content. This establishes a consistent max-width and spacing for the content.
While the FormSection is typically used to contain Form Fields, it can also be used to contain and set a consistent max-width for other content as needed such as an Alert.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Alert @type="inline" @color="critical" as |A|>
<A.Title @tag="h2">Form submission error</A.Title>
<A.Description>Correct the formatting of the following field:</A.Description>
<A.Description>
<Hds::Link::Inline @href="#" @color="secondary">Expiration date</Hds::Link::Inline>
</A.Description>
</Hds::Alert>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field name="field-1-name" as |F|>
<F.Label>Field 1</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
<Hds::Form::Radio::Group @layout="horizontal" @name="field-2-name" as |G|>
<G.Legend>Field 2</G.Legend>
<G.RadioField as |F|>
<F.Label>Option 1</F.Label>
</G.RadioField>
<G.RadioField as |F|>
<F.Label>Option 2</F.Label>
</G.RadioField>
<G.RadioField as |F|>
<F.Label>Option 3</F.Label>
</G.RadioField>
</Hds::Form::Radio::Group>
<Hds::Form::Select::Field name="field-3-name" as |F|>
<F.Label>Field 3</F.Label>
<F.Options>
<option value="Kubernetes">Kubernetes</option>
<option value="Other" selected>Selected</option>
</F.Options>
</Hds::Form::Select::Field>
<Hds::Form::Textarea::Field name="field-4-name" as |F|>
<F.Label>Field 4</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::Textarea::Field>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Pass an isFullWidth argument to override the default max-width of an individual FormSection if needed.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section @isFullWidth={{true}}>
<Hds::Form::RadioCard::Group @name="radio-card-basic-example" @alignment="center" as |G|>
<G.Legend>Create connection</G.Legend>
<G.RadioCard @checked={{true}} {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="aws-color" />
<R.Label>Quick peering with Quick Links</R.Label>
<R.Badge @text="2-5 min" />
<R.Description>Quick peering with quick links will provide the fastest way to connect to your providers’ network.</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
<G.RadioCard {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="aws-color" />
<R.Label>Manual peering using AWS CLI</R.Label>
<R.Badge @text="5-10 min" />
<R.Description>Provide you AWS CLI template to apply connection settings.</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
<G.RadioCard {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="hcp" />
<R.Label>Manual peering using HCP and AWS web console</R.Label>
<R.Badge @text="30-60 min" />
<R.Description>Manually follow UI instructions to complete configuring a connection at provider side.</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
</Hds::Form::RadioCard::Group>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Section Header, Title, & Description
Similarly to the Form, each FormSection can optionally include its own SectionHeader with Title and Description.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<FORM.SectionHeader>
<FORM.SectionHeaderTitle @tag="h3">Section header title</FORM.SectionHeaderTitle>
<FORM.SectionHeaderDescription>
Section Header description
</FORM.SectionHeaderDescription>
</FORM.SectionHeader>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Section Header Title tag & size
The @tag argument changes the HTML element that wraps the SectionHeaderTitle content. When organizing the content on a webpage, the heading levels should reflect the structure of the page. For example, if the FormHeaderTitle tag is "h3", the Section Title should be "h4".
To specify which size the SectionHeaderTitle displays at, use the @size argument.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<FORM.SectionHeader>
<FORM.SectionHeaderTitle @tag="h4" @size="200">Section header title</FORM.SectionHeaderTitle>
<FORM.SectionHeaderDescription>
Section Header description
</FORM.SectionHeaderDescription>
</FORM.SectionHeader>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Section Multi Field Group
To lay out related Form Fields or controls in a row, use the SectionMultiFieldGroup.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>First name</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>Last name</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
To control the widths of individual elements within a SectionMultiFieldGroup, you can wrap the element with an Item and pass in a width value. Fields not wrapped with an Item will take up the remaining available width.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup as |FG|>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>City</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
<FG.Item @width="auto">
<Hds::Form::Select::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>State</F.Label>
<F.Options>
<option value="state-1">Ohio</option>
<option value="state-2">Massachusetts</option>
<option value="state-3">Washington</option>
<option value="state-4">Florida</option>
<option value="state-4">North Carolina</option>
</F.Options>
</Hds::Form::Select::Field>
</FG.Item>
<FG.Item @width="8em">
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>Zip</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FG.Item>
</FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Form Separator
If further visual separation between Form Sections is desired, add a FormSeparator in-between.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Text::Body>First section</Hds::Text::Body>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Separator />
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Text::Body>Second section</Hds::Text::Body>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Responsive layout
In screen widths below 768px (the “md” breakpoint), the SectionMultiFieldGroup content layout will automatically stack.
<Hds::Form class="doc-form-layout-mobile-view" as |FORM|>
<FORM.Section>
<FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup as |FG|>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>City</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
<FG.Item @width="auto">
<Hds::Form::Select::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>State</F.Label>
<F.Options>
<option value="state-1">Ohio</option>
<option value="state-2">Massachusetts</option>
<option value="state-3">Washington</option>
<option value="state-4">Florida</option>
<option value="state-4">North Carolina</option>
</F.Options>
</Hds::Form::Select::Field>
</FG.Item>
<FG.Item @width="6em">
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>Zip</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FG.Item>
</FORM.SectionMultiFieldGroup>
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Form Footer
The FormFooter should be used at the bottom of the other Form content to contain form actions. Use the yielded ButtonSet to wrap and set spacing for Buttons.
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Footer as |FF|>
<FF.ButtonSet>
<Hds::Button @text="Submit" type="submit" />
<Hds::Button @text="Cancel" @color="secondary" />
</FF.ButtonSet>
</FORM.Footer>
</Hds::Form>
Putting it all together
An example form with Sections using the default max-width together with a full-width Section:
<Hds::Form as |FORM|>
<FORM.Header as |FH|>
<FH.Title @tag="h2">Add policy</FH.Title>
<FH.Description>
Please specify which policy you would like to assign to your cluster.
Read more about policies in our <Hds::Link::Inline @href="#">documentation</Hds::Link::Inline>.
</FH.Description>
</FORM.Header>
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field name="demo-secret-id" as |F|>
<F.Label>Secret ID</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>
Create a token within your self-managed cluster and attach
only the “builtin/global-read-only” policy to it. Once complete, save
the token, copy its secret ID from the token list, and insert it
below.
</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Section @isFullWidth={{true}}>
<Hds::Form::RadioCard::Group @name="demo-radio-card-policies-example" @alignment="center" as |G|>
<G.Legend>Policy framework</G.Legend>
<G.RadioCard @checked={{true}} {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="terraform" />
<R.Label>Terraform policy</R.Label>
<R.Badge @text="New" @color="highlight" />
<R.Description>
Write policies in HCL that directly reference Terraform resources to enforce your compliance and security requirements.
</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
<G.RadioCard {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="hashicorp" />
<R.Label>Sentinel</R.Label>
<R.Description>
Write policies imperatively for attribute-based access control to enforce compliance and security requirements.
</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
<G.RadioCard {{on "change" this.onChange}} as |R|>
<R.Icon @name="opa" />
<R.Label>Open Policy Agent (OPA)</R.Label>
<R.Description>
Open-source, general-purpose policy engine that allows you to enforce fine-grained access control and decision-making across cloud-native environments.
</R.Description>
</G.RadioCard>
</Hds::Form::RadioCard::Group>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Section>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field as |F|>
<F.Label>Policy set name</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>
Valid characters include ASCII letters, numbers, as well
as spaces, periods (.), dashes (-), and underscores (_).
</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Separator />
<FORM.Section as |FS|>
<FS.Header as |FSH|>
<FSH.Title>Policy OPA </FSH.Title>
<FSH.Description>
Policy OPA is a governance rule that enforces specific access controls and compliance requirements
within the organization‘s infrastructure.
</FSH.Description>
</FS.Header>
<Hds::Form::TextInput::Field placeholder="e.g data.terraform.deny" as |F|>
<F.Label>Query</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>
The rule expression that the policy will evaluate.
<Hds::Link::Inline
@href="https://www.terraform.io/cloud-docs/policy-enforcement/opa"
@icon="external-link"
>
Learn more about defining OPA policies
</Hds::Link::Inline>.
</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::TextInput::Field>
</FORM.Section>
<FORM.Footer as |FF|>
<FF.ButtonSet>
<Hds::Button @text="Submit" type="submit" />
<Hds::Button @text="Cancel" @color="secondary" />
</FF.ButtonSet>
</FORM.Footer>
</Hds::Form>
Setting a custom max-width
If needed, you can set a custom max-width for all Form Sections and other content at once vs. overriding the default max-width Section by Section.
<Hds::Form @sectionMaxWidth="100%">
<!-- Sections, FormHeader, FormFooter, and FormSeparators will all have 100% max-width -->
</Hds::Form>
If you set a custom max-width for Form content, you can still override it on an individual Section allowing certain Sections to expand to full width.
<Hds::Form @sectionMaxWidth="36rem" as |FORM|>
<!-- Sections, FormHeader, FormFooter, and FormSeparators will all have 36rem max-width -->
<FORM.Section @isFullWidth={{true}}>
<!-- Except this Section, which will have 100% max-width -->
</FORM.Section>
</Hds::Form>
Component API
Form
<[F].Header>
yielded component
Form::Header yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].HeaderTitle>
yielded component
Form::Header::Title yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].HeaderDescription>
yielded component
[Form::Header::Description yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].Section>
yielded component
Form::Section yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].SectionHeader>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].SectionHeaderTitle>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header::Title yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].SectionHeaderDescription>
yielded component
Form::.Section::Header::Description yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].SectionMultiFieldGroup>
yielded component
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].SectionMultiFieldGroupItem>
yielded component
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup::Item yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].Separator>
yielded component
Form::Separator yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[F].Footer>
yielded component
Form::Footer yielded as contextual component (see below).
tag
enum
- form (default)
- div
Form content.
sectionMaxWidth
string
Form Section components and other direct Form child components which include the FormHeader, FormSeparator, and FormFooter.
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Header
<[FH].Title>
yielded component
Form::Header::Title yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FH].Description
yielded component
Form::Header::Description yielded as contextual component (see below).
isFullWidth
boolean
- false (default)
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Header::Title
tag
enum
- div (default)
- h1
- h2
- h3
- h4
- h5
- h6
Title element.
size
string
- 500
- 400
- 300
- 200 (default)
- 100
Display text style.
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Header::Description
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Section
<[FS].Header>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FS].HeaderTitle>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header::Title yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FS].HeaderDescription>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header::Description yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FS].MultiFieldGroup>
yielded component
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FS].MultiFieldGroupItem>
yielded component
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup::Item yielded as contextual component (see below).
isFullWidth
boolean
- false (default)
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Section::Header
<[FSH].Title>
yielded component
Form::Section::Header::Title yielded as contextual component (see below).
<[FSH].Description
yielded component
Form::Section::Header::Description yielded as contextual component (see below).
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup
<[MFG].Item>
yielded component
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroup::Item yielded as contextual component (see below).
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Section::MultiFieldGroupItem
width
string
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Separator
isFullWidth
boolean
- false (default)
…attributes
...attributes.
Form::Footer
<[FF].ButtonSet>
yielded component
[ButtonSet](/component/button-set] yielded as contextual component
isFullWidth
boolean
- false (default)
yield
…attributes
...attributes.
Anatomy
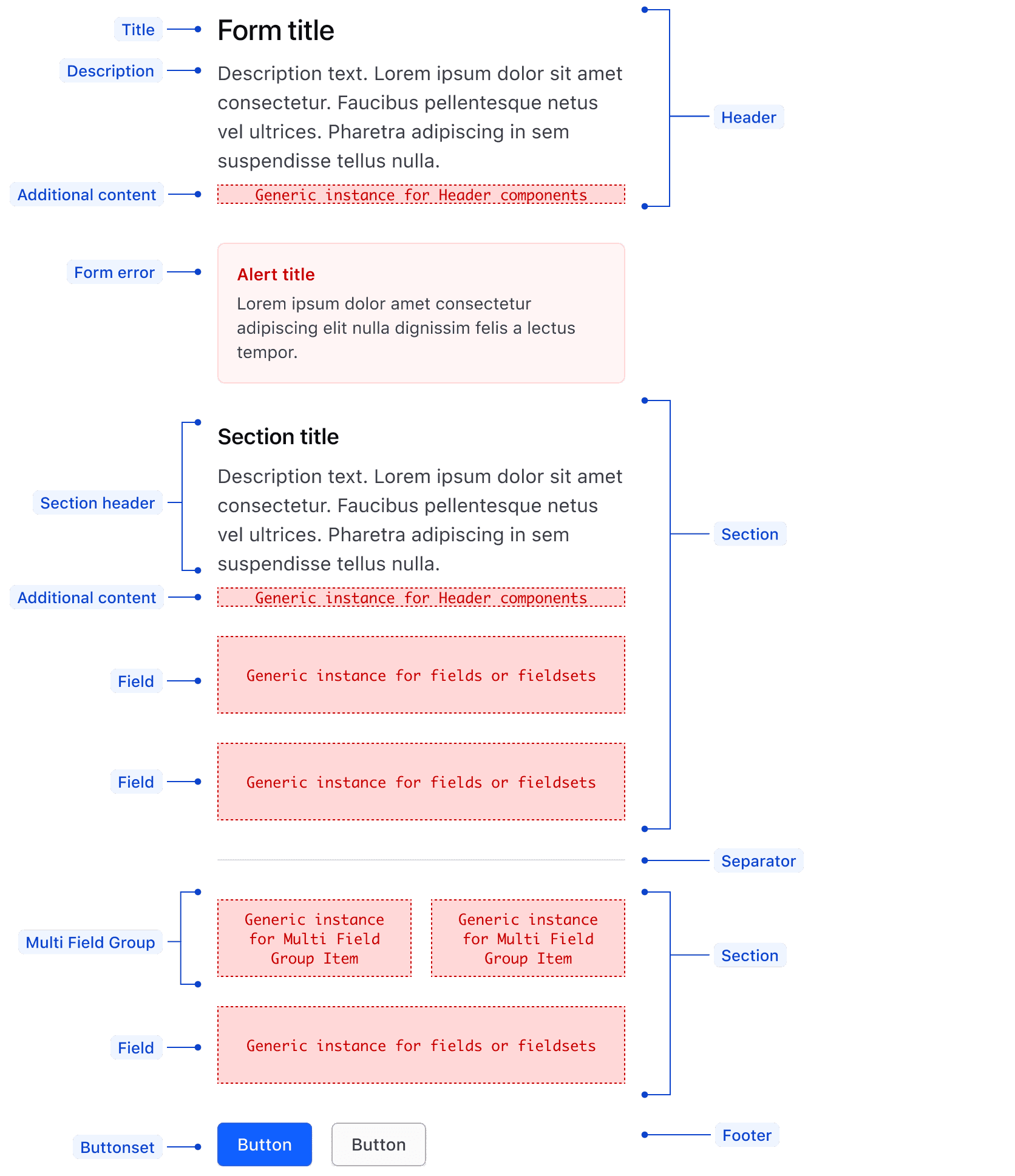
| Element | Usage |
|---|---|
| Title/Section title | Optional |
| Description/Section description | Optional |
| Section | May consist of multiple content types, including text, fields, and multi field groups. |
| Form error | Optional, uses the critical inline Alert |
| Field | Required, supports any Form component |
| Multi Field Group | Optional, supports any Form component |
| Separator | Optional |
| Footer | Most often consists of ButtonSet and actions |
Spacing
Spacing in forms is based on a decreasing scale on an 8px grid. From largest to smallest, the spacing structure is:
- The Form Header, Sections, Separators, and Footer are 32px apart.
- Stacked inputs are 24px apart.
- Side by side inputs within a Section Multi Field Group are 16px apart.
- Text elements within the Form Header and Form Section Headers are 8px apart.
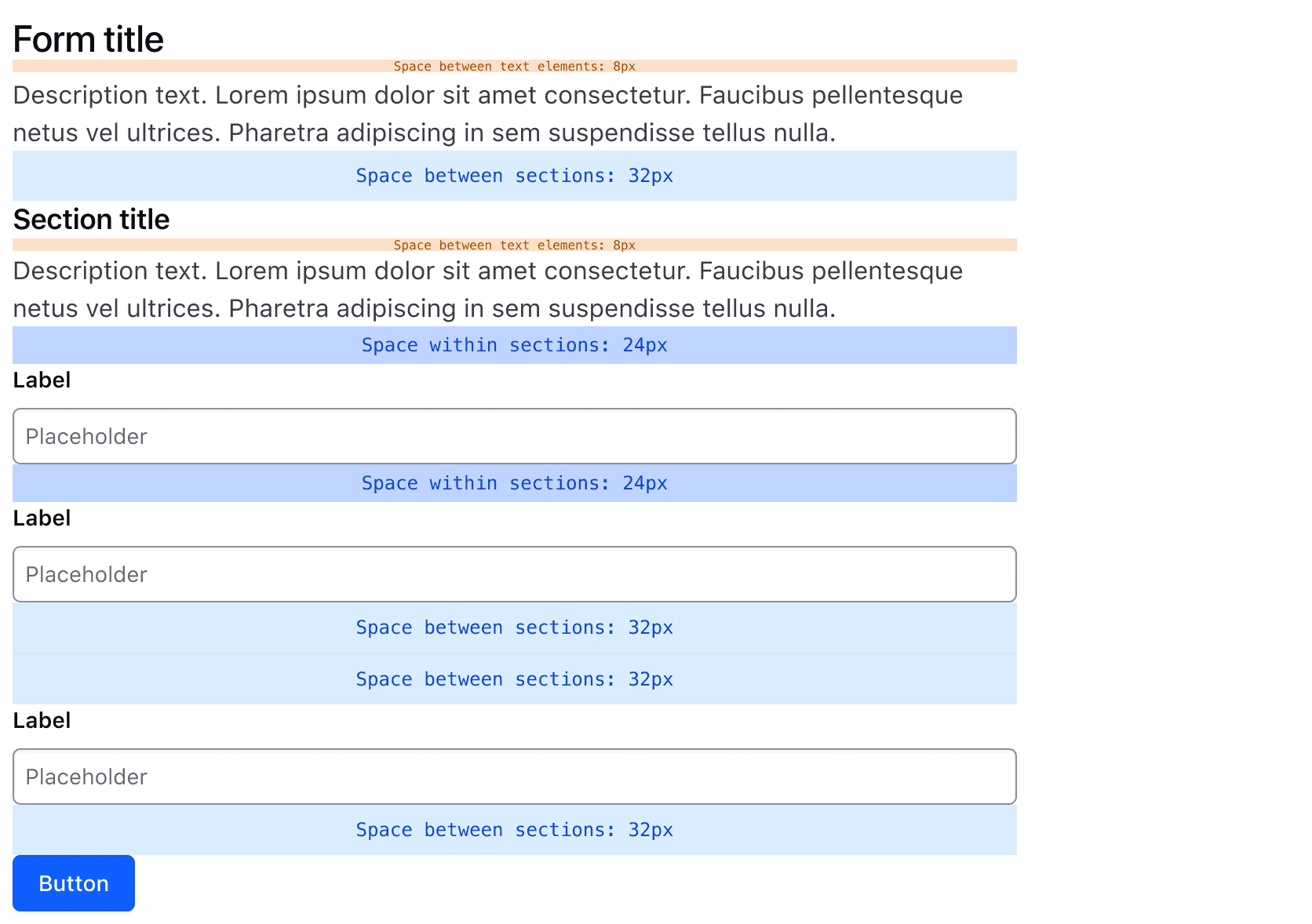
Visit the Form Patterns guidelines for additional details on spacing in forms.
Conformance rating
When used as recommended, there should not be any WCAG conformance issues with this component.
Applicable WCAG Success Criteria
This section is for reference only. This component intends to conform to the following WCAG Success Criteria:
-
1.3.2
Meaningful Sequence (Level A):
When the sequence in which content is presented affects its meaning, a correct reading sequence can be programmatically determined. -
1.4.10
Reflow (Level AA):
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions. -
1.4.12
Text Spacing (Level AA):
No loss of content or functionality occurs by setting all of the following and by changing no other style property: line height set to 1.5; spacing following paragraphs set to at least 2x the font size; letter-spacing set at least 0.12x of the font size, word spacing set to at least 0.16 times the font size. -
1.4.4
Resize Text (Level AA):
Except for captions and images of text, text can be resized without assistive technology up to 200 percent without loss of content or functionality. -
2.4.3
Focus Order (Level A):
If a Web page can be navigated sequentially and the navigation sequences affect meaning or operation, focusable components receive focus in an order that preserves meaning and operability. -
2.4.7
Focus Visible (Level AA):
Any keyboard operable user interface has a mode of operation where the keyboard focus indicator is visible. -
2.4.11
Focus Not Obscured (Minimum) (Level AA):
When a user interface component receives keyboard focus, the component is not entirely hidden due to author-created content.
Support
If any accessibility issues have been found within this component, let us know by submitting an issue.
4.21.0
Form - Added Form component and related sub-components for form layout
